The Evolution and Impact of Medical Technology

Introduction
Medical technology has revolutionized healthcare, transforming the way diseases are diagnosed, treated, and prevented. From advanced imaging techniques to innovative surgical tools and digital health solutions, medical technology continues to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery. This article explores the key advancements in medical technology, their benefits, and the future of this dynamic field.
Key Advancements in Medical Technology
- Imaging and Diagnostic Tools
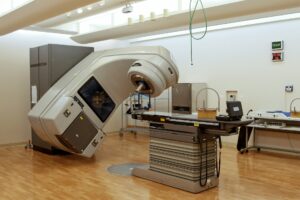
- MRI and CT Scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans have significantly enhanced diagnostic accuracy. These imaging techniques provide detailed images of the body’s internal structures, helping in the early detection of diseases like cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological disorders.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound technology uses sound waves to produce real-time images of organs and tissues. It is widely used in prenatal care, cardiology, and emergency medicine.
- PET Scans: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans detect metabolic activity in tissues, aiding in the diagnosis and management of cancers, brain disorders, and heart diseases.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Laparoscopy: Laparoscopic surgery involves small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments. It reduces recovery time, minimizes pain, and lowers the risk of complications compared to traditional open surgery.
- Robotic Surgery: Robotic-assisted surgery provides surgeons with greater precision, flexibility, and control. Systems like the da Vinci Surgical System are used in procedures ranging from urology to gynecology and cardiac surgery.
- Advanced Therapeutics
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies use drugs to target specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression. This approach minimizes damage to healthy cells and improves treatment efficacy.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy enhances the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Techniques like CAR-T cell therapy have shown promising results in treating certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
- Gene Therapy: Gene therapy involves modifying genes to treat or prevent diseases. Recent advancements have led to successful treatments for genetic disorders like spinal muscular atrophy and certain types of blindness.
- Wearable and Remote Monitoring Devices
- Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers: Devices like smartwatches monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. They provide real-time health data, encouraging proactive health management.
- Remote Monitoring Systems: These systems allow healthcare providers to monitor patients’ conditions remotely. They are particularly beneficial for managing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart failure.
- Telemedicine
- Virtual Consultations: Telemedicine platforms enable patients to consult with healthcare providers via video calls, reducing the need for in-person visits. This has proven invaluable during the COVID-19 pandemic and for individuals in remote areas.
- Digital Health Records: Electronic Health Records (EHRs) streamline patient data management, improving coordination among healthcare providers and enhancing patient care.
Benefits of Medical Technology
- Improved Diagnosis and Treatment: Advanced diagnostic tools and therapeutic techniques lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, resulting in more effective treatments and better patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Minimally invasive surgical techniques and precise robotic systems reduce the risk of complications, infection, and prolonged hospital stays.
- Increased Accessibility: Telemedicine and remote monitoring devices make healthcare more accessible to individuals in rural or underserved areas, ensuring timely medical attention.
- Cost-Effective Care: By reducing the need for hospitalization and in-person visits, medical technology helps lower healthcare costs for both patients and providers.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics and biotechnology enable personalized treatment plans tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects.
The Future of Medical Technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are poised to revolutionize diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine. AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make accurate predictions, aiding in early disease detection and treatment planning.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing technology is being used to create custom prosthetics, implants, and even bioprinted organs. This technology promises to improve surgical outcomes and patient quality of life.
- Blockchain in Healthcare: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management, enhancing the privacy and integrity of patient records. It can also streamline supply chain management and reduce fraud.
- Nanotechnology: Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials at the nanoscale to develop targeted drug delivery systems, advanced diagnostic tools, and innovative treatments for various diseases.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell research and tissue engineering hold the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering new treatment options for conditions like heart disease, spinal cord injuries, and degenerative disorders.
Conclusion
Medical technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, transforming healthcare and improving patient outcomes. From advanced imaging and minimally invasive surgery to wearable devices and telemedicine, these innovations enhance diagnosis, treatment, and accessibility. As technologies like AI, 3D printing, and nanotechnology evolve, the future of medical technology promises even greater advancements, paving the way for a healthier and more connected world.