Diagnostic Imaging: An Essential Tool in Modern Medicine
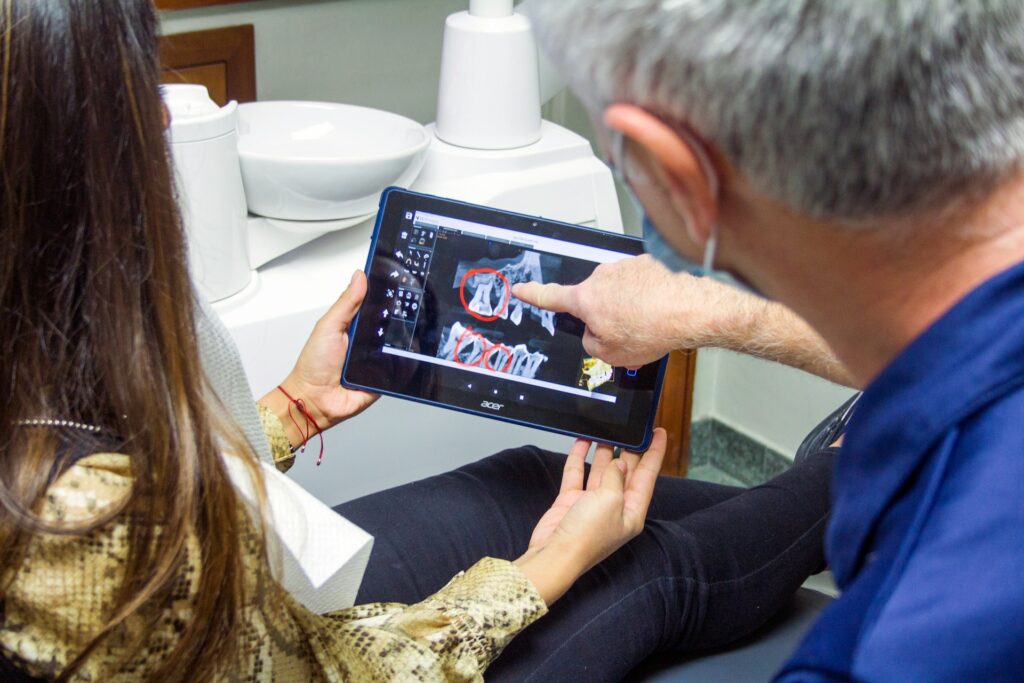

Introduction
Diagnostic imaging is a cornerstone of modern medical practice, providing crucial insights that guide the diagnosis, treatment, and management of various health conditions. By utilizing different imaging modalities, healthcare professionals can visualize the internal structures and functions of the body non-invasively. This article explores the types, purposes, and advancements in diagnostic imaging.
Types of Diagnostic Imaging
1. X-ray Imaging
X-ray imaging is one of the oldest and most commonly used diagnostic tools. It involves passing X-rays through the body to produce images of bones and certain tissues. This modality is particularly useful in detecting fractures, infections, and tumors.
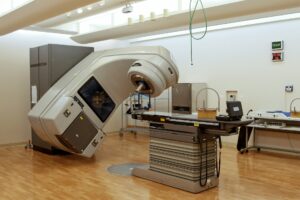
2. Computed Tomography (CT)
CT scans combine X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional views of the body. This technology provides more detailed information than standard X-rays, making it valuable for diagnosing conditions such as cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and internal injuries.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of organs and tissues. It is particularly useful for imaging soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and ligaments. MRI is a preferred method for detecting neurological disorders, musculoskeletal problems, and certain cancers.
4. Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of internal structures. It is widely used in obstetrics to monitor fetal development, as well as in cardiology, abdominal imaging, and guiding certain interventional procedures.
5. Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine involves the use of small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases. Techniques like positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) provide functional information about organs and tissues, which is invaluable in detecting cancers, heart disease, and other conditions.
Purposes of Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging serves several key purposes in medical practice:
- Diagnosis: It helps in identifying the presence and extent of diseases and conditions.
- Treatment Planning: Imaging guides the planning of surgeries, radiation therapy, and other treatments.
- Monitoring: It is used to monitor the progress of diseases and the effectiveness of treatments.
- Screening: Imaging can detect diseases at an early, more treatable stage, such as mammograms for breast cancer screening.
Advancements in Diagnostic Imaging
The field of diagnostic imaging is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and research. Some notable developments include:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into imaging to enhance image analysis, improve diagnostic accuracy, and reduce the workload of radiologists. These technologies can identify patterns and anomalies that may be missed by the human eye.
2. 3D and 4D Imaging
3D imaging provides a more comprehensive view of anatomical structures, improving the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment plans. 4D imaging, which adds the dimension of time, allows for the visualization of dynamic processes, such as blood flow and organ motion.
3. Fusion Imaging
Fusion imaging combines information from different imaging modalities (e.g., PET/CT, PET/MRI) to provide more detailed and comprehensive diagnostic information. This approach enhances the ability to diagnose complex conditions.
4. Portable and Point-of-Care Imaging
The development of portable imaging devices has made it possible to perform diagnostic imaging in various settings, including remote areas, emergency rooms, and at the bedside. This enhances the accessibility and convenience of imaging services.
Conclusion
Diagnostic imaging is an indispensable component of modern healthcare, enabling accurate diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and efficient monitoring of medical conditions. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities and applications of diagnostic imaging will expand, further improving patient care and outcomes. The integration of AI, the advent of 3D and 4D imaging, and the development of portable imaging devices are just a few examples of how this field is evolving to meet the needs of contemporary medicine.